Observing Stations
Rio Gallegos, Argentina (51.6 S, 69.3 W)
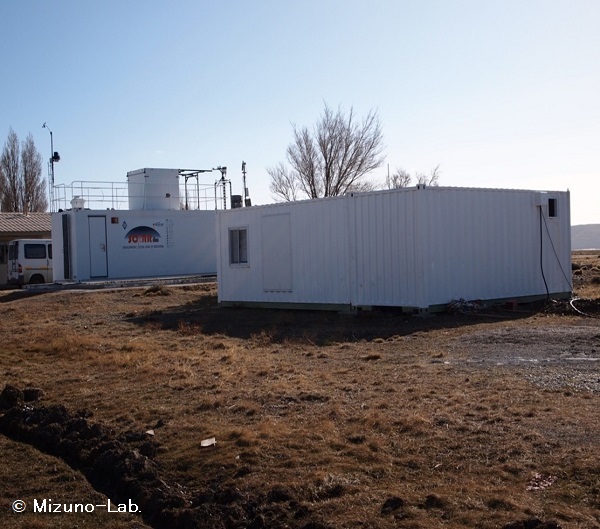

Observing sites in OAPA. The left-hand side container is ozone DIAL (Differencial Absorption Lidar) station, and the right-hand side container is mm-wave spectrometer station.
The South-Patagonian region in South America is the southernmost habitable area in the world, and the inhabitant of this region directly suffers the influence of ozone hole that overpasses the region during austral late spring. Observatorio Atmosferico de la Patagonia Austral (Atmospheric Observatory of Austral Patagonia: OAPA) in Rio Gallegos, Argentina is located near the tip of the South American continent. In order to study the vertical structure of the boundary region of ozone hole and its temporal variation, we installed a mm-wave spectrometer in 2010 in collaboration with Centro de Investigaciones en Laseres y Aplicaciones (Lasar Application and research Center: CEILAP) and started continuous monitoring of the stratospheric ozone at 110 GHz since 2012.
This project is financially supported by SATREPS (Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development) program promoted by JST and JICA (http://www.jst.go.jp/global/english/kadai/h2404_argentine.html).
